Page 6 - Surface Water Management Guidance - 2023
P. 6
3. The Benefits of Early Engagement 4. Main Pollutants
Companies who pre-plan their work activities to include for the protection of the environment can In relation to the development of Greenfield and Brownfield sites, there are four key water
reap a number of benefits; for example: pollutants which need to be considered by all sites where excavation into the ground is
required. These pollutants are:
• Increased profitability - works will be completed more efficiently using the correct amount of
resource, in a timely manner. • Silt laden water
• Better client relationships - resulting in smoother operation of the project and increased order • Alkaline pH
books; • Dissolved Metals
• Better stakeholder relationships - raising the profile of the company, promoting the company • Fuels and Oils
brand;
• Speedier and more appropriate response to any pollution incident - minimising its spread and A proactive site will manage these pollutants until such time that any permanent water treatment
environmental impact; systems (site drainage, suds systems etc) are installed and the risks of polluted water being released
• Better relationships with the Environmental Regulator-reducing the amoun to fregulatory scrutiny are eliminated.
on the company’s operations
4.1 Silt Laden Water
Whilst most companies do have an internal environmental management team, these teams cannot The release of turbid, cloudy, silt laden water into the aquatic environment, can have a large neg-
totally focus on the management of surface water and groundwater. They have responsibility for ative impact on the quality of inland water ways. Fine grained sediment may settle to the bed of
a wide range of activities such as archaeology, wildlife and habitats, emissions to air and waste the waterway, blind off gravels and destroy vital habitats.
minimisation.
The simple act of turning a water course cloudy may cause fish gills to become blocked, alter the
natural penetration of light, increase the temperature of the water body and/or cause a reduction
in oxygen levels.
4.2 Alkaline pH
The hydration of cement to make it set, causes Council and Contractor in
a dramatic increase in the pH of water that Court following pollution
comes into contact with it i.e. wash water, run- resulting from bridge
off from recently poured areas of concrete. Also, strengthening works.
the use of hydro-demolition to cut concrete will
cause an increase in the pH of the blast water. A new concrete structure was need-
ed to strengthen the bridge, the
Frequently, the pH will be in the region of pH12 works should have been carried out
to 13, a similar pH to oven cleaner. in dry conditions. Water came into
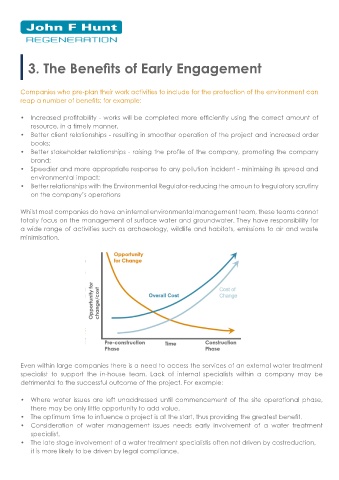
Even within large companies there is a need to access the services of an external water treatment contact with curing concrete.
specialist to support the in-house team. Lack of internal specialists within a company may be The pH range typical of inland waters is in the
detrimental to the successful outcome of the project. For example:
region pH 6 to 9, and for discharge to foul The Court heard that cement is
sewers is typically pH 5 to 10. highly alkaline and can be fatal to
• Where water issues are left unaddressed until commencement of the site operational phase, fish. The stream turned milky white in
there may be only little opportunity to add value. The aquatic environment is very sensitive to colour and had an elevated pH.
• The optimum time to influence a project is at the start, thus providing the greatest benefit. pH, and even small changes can have a
• Consideration of water management issues needs early involvement of a water treatment widespread impact on biodiversity. Dead fish were reported over a
specialist. 1.5km stretch downstream of the
• The late stage involvement of a water treatment specialistis often not driven by costreduction, bridge. Some 4,000 fish were killed.
it is more likely to be driven by legal compliance.